You’re not imagining it. And you’re definitely not alone.
If you’ve been avoiding the beach, wearing baggy shirts, or feeling self-conscious in locker rooms, you’re dealing with something that affects a majority of men at some point in their lives. It’s called gynecomastia, and it’s way more common than anyone talks about.
The medical term might sound intimidating, but the condition itself is pretty straightforward: enlarged male breast tissue. What’s not straightforward is figuring out why it happened and what you can actually do about it.
What’s Really Going On (And Why It Happens)
Here’s the thing about gynecomastia—it’s not just about being out of shape. There are actually two different types of male breast enlargement, and understanding which one you have makes all the difference in treatment.
True gynecomastia happens when you develop actual glandular breast tissue. This feels firm or rubbery right behind your nipple, almost like a small mass. It’s caused by hormonal imbalances—specifically, when estrogen levels get too high relative to testosterone.
Pseudogynecomastia is different. This is just excess fat in your chest area, with no actual glandular tissue development. It feels soft, like fat anywhere else on your body.
Most guys actually have a combination of both.
The hormonal piece is interesting. All men produce both testosterone and estrogen, but testosterone usually keeps things in check. When that balance shifts—either because estrogen goes up or testosterone drops—breast tissue can start growing.
The Usual Suspects: What Causes This to Happen
Sometimes, gynecomastia is just part of life’s natural progression. About 60% of teenage boys develop some degree of it during puberty, though it usually resolves on its own within three years. Similarly, up to 65% of older men experience it as testosterone naturally declines with age.
But there are other culprits worth knowing about:
Your body fat percentage plays a huge role. Fat tissue contains an enzyme called aromatase that literally converts testosterone into estrogen. The more body fat you carry, the more this conversion happens.
Before & After Photos
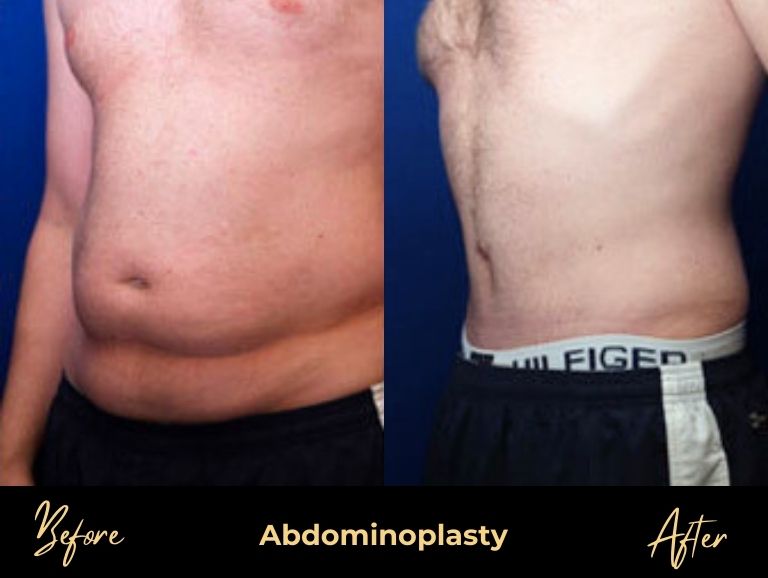
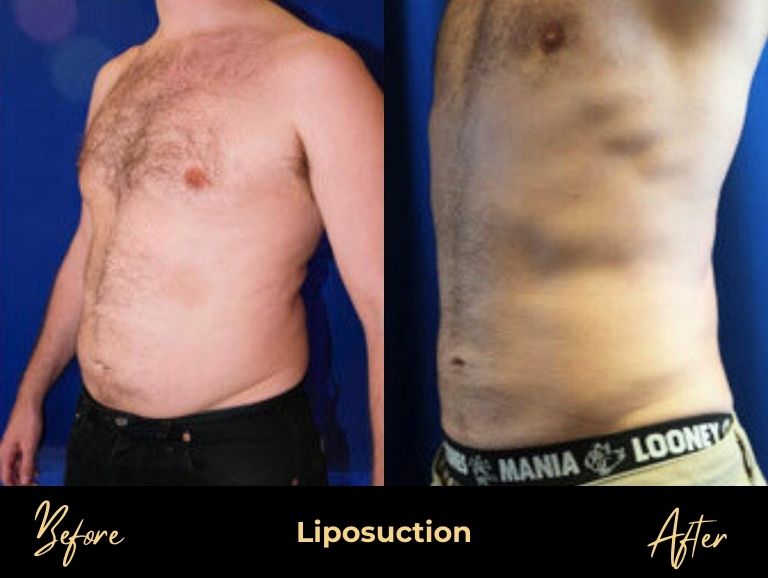
men's Procedures
Before & After Photos

men's Procedures
Medications and substances cause about 20% of cases. The list includes alcohol (a big one), certain blood pressure medications, some antidepressants, and, unfortunately, anabolic steroids, which is ironic, considering why most guys take them in the first place.
Medical conditions can also trigger it. Thyroid problems, liver or kidney issues, and certain hormonal disorders all disrupt the testosterone-estrogen balance.
What You Can Try Before Surgery
Before jumping to surgical solutions, there are several approaches worth attempting, especially if your case is mild or recent.
Lifestyle Changes That Actually Work
Diet and exercise aren’t cure-alls, but they can make a significant difference, particularly for the fat component. Here’s what actually moves the needle:
- Strength training builds chest muscle underneath, which can improve the overall contour
- Cardio reduces overall body fat percentage (you can’t spot-reduce, but lowering overall fat helps)
- Limiting alcohol removes a major estrogen-boosting factor
- Getting quality sleep supports healthy testosterone production
Most guys see changes after about 8 weeks of consistent effort.
When Surgery Becomes the Answer
For many men, gynecomastia surgery is the most effective and permanent solution. Male breast reduction combines two techniques based on what type of tissue needs to be removed.
Liposuction handles the fat component through small, discreet incisions. Recovery is faster, scarring is minimal, but it can’t address glandular tissue.
Surgical excision removes the actual glandular tissue through an incision around the areola. This prevents recurrence more effectively but involves more recovery time and visible scarring.
The gold standard approach combines both techniques. By using liposuction for fat and excision for glandular tissue, surgeons can address both causes while minimizing recurrence risk—which drops to just 2% with combined treatment versus 6% with liposuction alone.
The Real Impact (Beyond the Physical)
The psychological benefits often surprise guys. Studies consistently show significant improvements in self-esteem, social functioning, and overall mental health after surgery. Men report feeling confident enough to participate in activities they’d been avoiding for years.
Even when minor complications occur—like small blood collections or residual tissue—satisfaction rates remain extremely high because the quality of life improvements are so substantial.
What the Surgery Actually Involves
If you decide surgery is right for you, here’s what the timeline typically looks like:
- Day 1: You’ll wear a compression garment to minimize swelling. Expect soreness similar to an intense chest workout.
- Days 2-3: Movement gets easier, though you’ll keep wearing the compression garment. Most guys with desk jobs return to work in about a week.
- Week 1: Light cardio like walking becomes okay.
- Week 1-6: Patients wear compression garments 3 weeks, 24/7 and then 3 weeks during sleep.
- Month 1: Full upper body workouts are usually cleared.
- Month 2: About 80% of the results are visible after 2 months; improvement continues until about 6 months after surgery, when all swelling should be gone.
- One year: All swelling is gone, and incisions have faded significantly.
The Financial Reality
The average “surgeon’s”all-inclusive” (anesthesia, facility costs, post-surgery garments, etc.) fee for this surgery in the San Francisco Bay Area runs between $7,000 – $15,000. Most insurance plans won’t cover this unless it meets strict “medical necessity” criteria—which includes things like the condition persisting for over a year, ruling out other causes, and trying conservative treatments first.
When considering any surgeon, make sure you’re getting comprehensive, all-inclusive pricing for gynecomastia surgery to avoid surprise costs later.
Finding the Right Surgeon
This isn’t a procedure you want to bargain hunt for. Look for a board-certified plastic surgeon with specific experience in male breast reduction. Check their credentials, review before-and-after photos, and make sure they operate in an accredited facility.
The consultation should feel thorough and educational, not rushed or sales-focused. A good surgeon will discuss all your options—surgical and non-surgical—and help you understand which approach makes sense for your specific situation.
The Bottom Line
Gynecomastia is incredibly common, but that doesn’t make dealing with it any easier. Whether you pursue lifestyle changes, medical treatment, or surgery, the key is understanding your options and working with qualified professionals who take your concerns seriously.
You don’t have to live with something that affects your confidence and quality of life. With the right approach, most men see significant improvement and wonder why they waited so long to address it.
The first step is simply having an honest conversation with a qualified physician about what’s possible in your specific case. From there, you can make an informed decision about the path that makes sense for you.


